Human health is a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors that influence our overall well-being and longevity. Understanding health problems and developing effective mitigation strategies is crucial for enhancing life quality and expectancy. This article explores common health problems, their underlying causes, and evidence-based strategies for living a longer and healthier life.
I. Understanding Human Health
1. Dimensions of Health

Human health encompasses several dimensions:
- Physical Health: Refers to the efficient functioning of the body and its systems.
- Mental Health: Involves emotional and psychological well-being.
- Social Health: Relates to the ability to form satisfying interpersonal relationships.
- Spiritual Health: Connects to finding meaning and purpose in life.
- Environmental Health: Involves the impact of environmental factors on health.
2. Determinants of Health

Several factors determine health outcomes:
- Genetics: Inherited traits that influence susceptibility to certain conditions.
- Lifestyle: Behaviors such as diet, physical activity, and substance use.
- Environment: Physical, chemical, and biological factors affecting health.
- Healthcare Access: Availability and quality of medical care and preventive services.
- Social and Economic Factors: Education, income, and social support networks.
II. Common Health Problems
1. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs)
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death globally. They include conditions such as coronary artery disease, stroke, and hypertension.
- Causes: Risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle.
- Symptoms: Symptoms vary but may include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
2. Cancer

Cancer encompasses a range of diseases characterized by uncontrolled cell growth. It can affect any part of the body, with common types including breast, lung, and colorectal cancer.
- Causes: Genetic mutations, lifestyle factors (such as smoking and diet), and environmental exposures (like radiation).
- Symptoms: Symptoms depend on the cancer type but may include lumps, unexplained weight loss, and persistent cough.
3. Respiratory Diseases
Chronic respiratory diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma affect the airways and lungs.
- Causes: Smoking, air pollution, occupational exposures, and genetic predisposition.
- Symptoms: Shortness of breath, wheezing, and chronic cough.
4. Diabetes

Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body cannot effectively regulate blood sugar levels. Types include Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes.
- Causes: Genetics, obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet.
- Symptoms: Increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
5. Mental Health Disorders

Mental health disorders include depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.
- Causes: Genetic factors, brain chemistry, trauma, and stress.
- Symptoms: Vary widely but can include mood changes, withdrawal from social activities, and cognitive impairments.
6. Obesity

Obesity is a condition characterized by excessive body fat, increasing the risk of various health issues.
- Causes: Poor diet, physical inactivity, genetic factors, and certain medications.
- Symptoms: Excessive body weight, fatigue, and difficulty with physical activities.
III. Mitigation Strategies
1. Balanced Nutrition
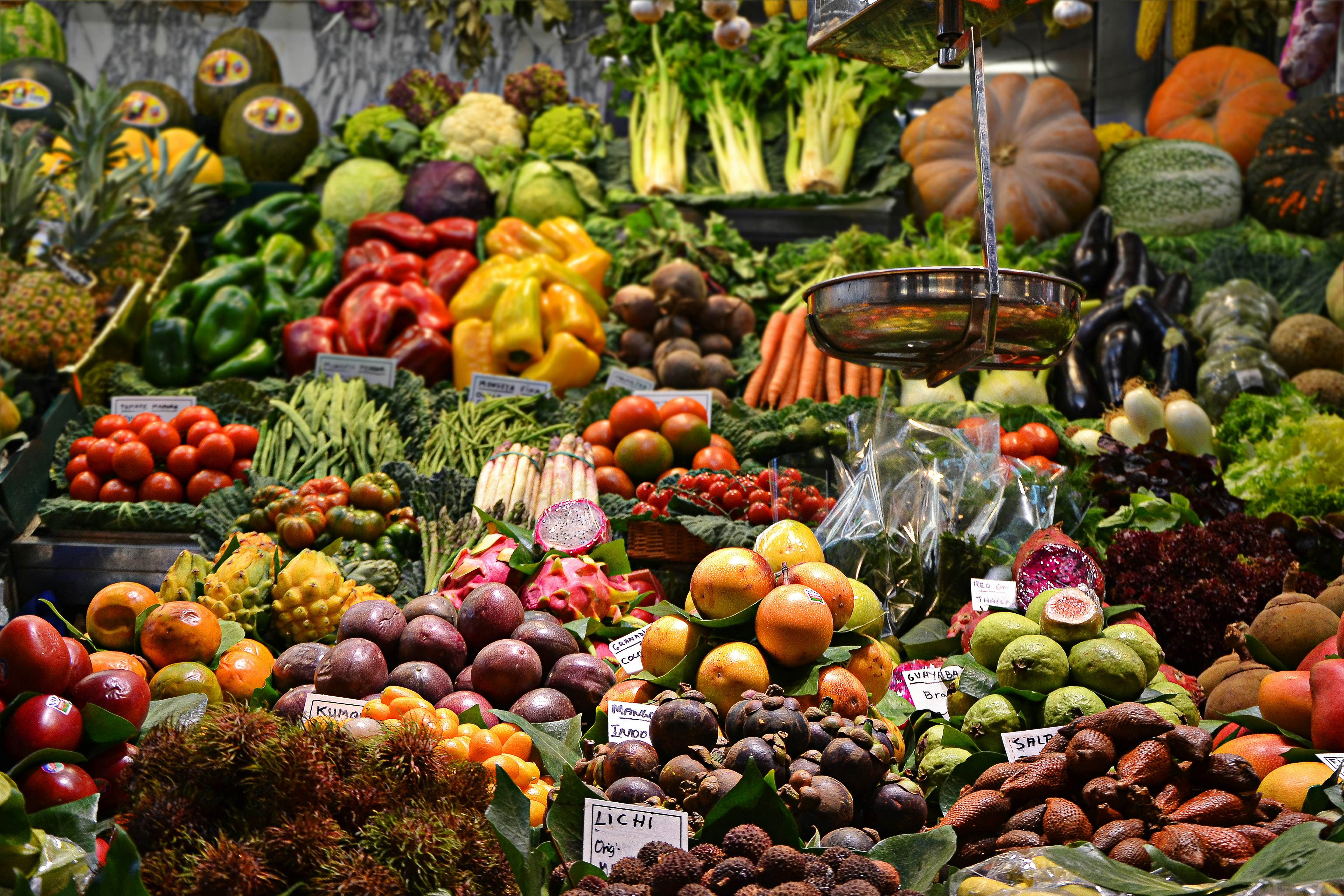

Diet plays a critical role in maintaining health and preventing diseases.
Principles of Balanced Diet:
- Variety: Incorporate diverse food groups.
- Moderation: Avoid excessive intake of any single type of food.
- Nutrient-Density: Choose foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Components:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Whole Grains: Source of complex carbohydrates and fiber.
- Lean Proteins: Include fish, poultry, beans, and nuts.
- Healthy Fats: Focus on unsaturated fats from sources like olive oil and avocados.
- Limited Sugars and Saturated Fats: Reduce intake of processed foods and sugary drinks.
2. Regular Physical Activity
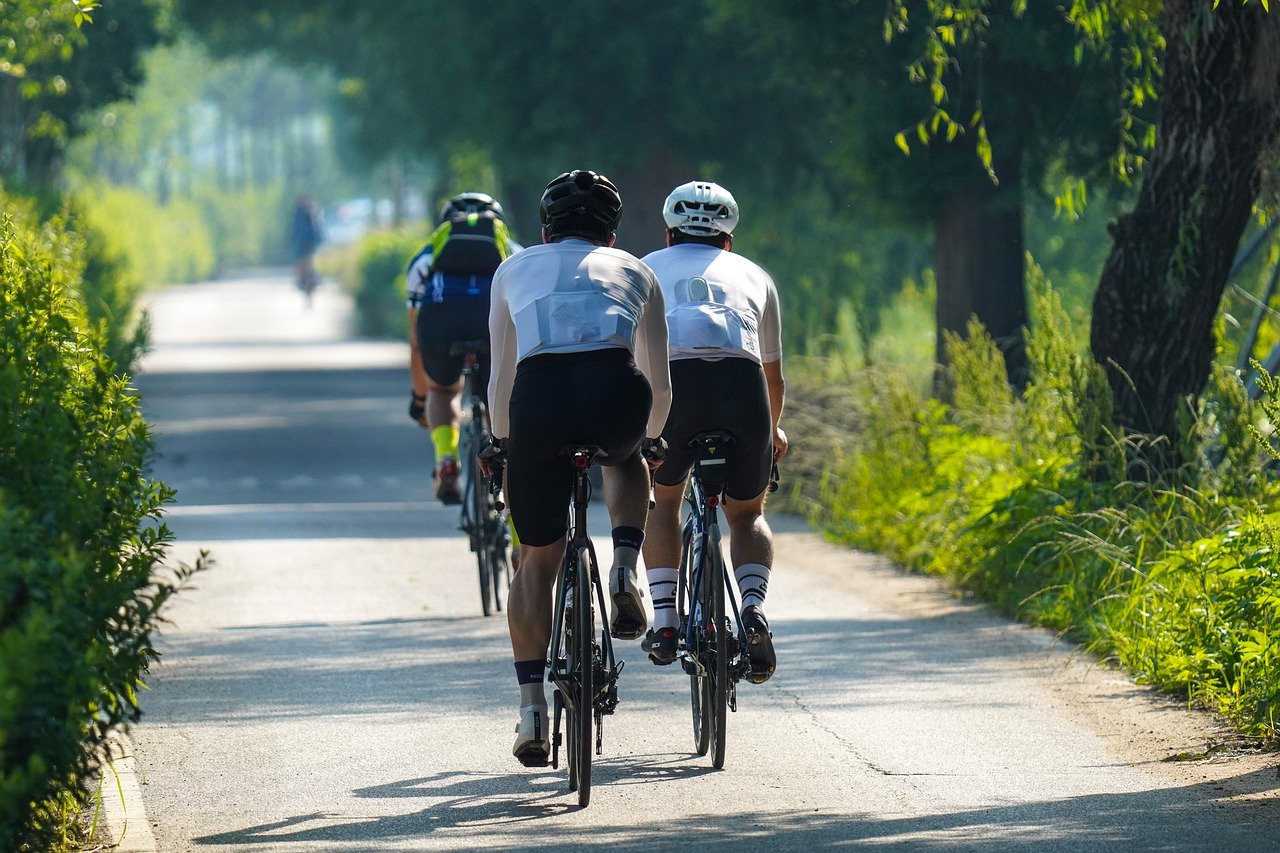

Physical activity is vital for maintaining cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and overall well-being.
Types of Exercise:
- Aerobic Exercise: Such as walking, running, and swimming, improves cardiovascular health.
- Strength Training: Builds muscle mass and bone density.
- Flexibility Exercises: Enhance joint mobility and reduce injury risk.
- Balance Training: Helps prevent falls, especially in older adults.
Recommendations:
- Adults: At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of high-intensity exercise per week, plus strength training twice weekly.
- Children: At least 60 minutes of physical activity per day.
3. Mental Health Care

Mental well-being is essential for overall health. Strategies include:
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can reduce stress.
- Social Support: Building strong relationships and social networks provides emotional support.
- Professional Help: Seeking therapy or counseling for persistent mental health issues.
4. Preventive Healthcare
Preventive healthcare involves regular screenings and vaccinations to detect and prevent diseases early.
- Screenings:
- Cardiovascular Screenings: Monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and glucose levels.
- Cancer Screenings: Includes mammograms, colonoscopies, and skin checks.
- Diabetes Screenings: Regular blood sugar testing for at-risk individuals.
- Vaccinations:
- Childhood Vaccinations: Protect against diseases like measles, mumps, and rubella.
- Adult Vaccinations: Includes flu shots, tetanus boosters, and vaccinations for shingles and pneumonia.
5. Tobacco and Alcohol Control
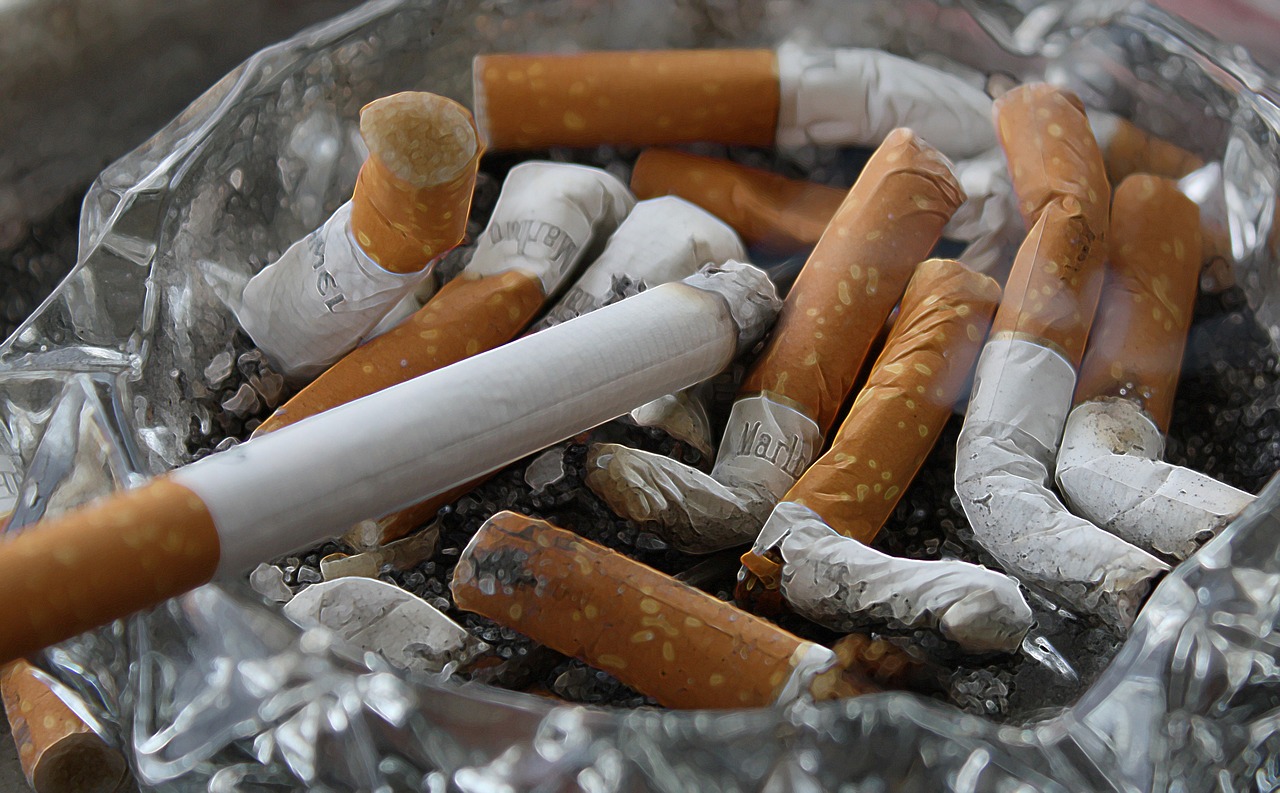

Avoiding tobacco and limiting alcohol consumption are crucial for preventing numerous health problems.
- Tobacco: Smoking cessation reduces the risk of cancer, respiratory diseases, and cardiovascular problems.
- Alcohol: Limiting alcohol intake lowers the risk of liver disease, certain cancers, and addiction.
6. Sleep Hygiene

Quality sleep is essential for physical and mental health.
- Sleep Recommendations:
- Adults: 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
- Children and Adolescents: Varies by age, generally 9-12 hours for school-age children.
- Sleep Hygiene Practices:
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day.
- Comfortable Sleep Environment: Ensure a quiet, dark, and cool room.
- Avoid Stimulants: Reduce caffeine and electronic device use before bed.
7. Environmental Health

Environmental factors significantly impact health.
- Air Quality: Reduce exposure to pollutants by using air purifiers and avoiding outdoor activities on high pollution days.
- Water Quality: Ensure access to clean drinking water.
- Toxic Exposures: Limit exposure to harmful chemicals and substances in the home and workplace.
IV. Strategies for Specific Populations
 1. Children and Adolescents
1. Children and Adolescents
Children and adolescents require specific health strategies to support growth and development.
- Nutrition: Balanced diet rich in nutrients for growth.
- Physical Activity: Daily exercise to build strong bones and muscles.
- Mental Health: Supportive environments to foster emotional well-being.
- Safety: Injury prevention measures such as seat belts and helmets.
2. Adults
Adults face diverse health challenges, requiring a tailored approach.
- Chronic Disease Management: Regular monitoring and management of conditions like hypertension and diabetes.
- Work-Life Balance: Strategies to manage stress and maintain mental health.
- Preventive Care: Regular health screenings and vaccinations.
3. Older Adults
Older adults have unique health needs to maintain independence and quality of life.
- Mobility and Strength: Exercises to maintain physical function and prevent falls.
- Nutrition: Diet adjustments to meet changing nutritional needs.
- Cognitive Health: Activities to stimulate mental function and social engagement.
- Chronic Disease Management: Comprehensive care plans for managing multiple conditions.
V. Advances in Health Promotion
 1. Digital Health
1. Digital Health
Digital health technologies are transforming healthcare delivery.
- Telemedicine: Provides remote access to healthcare services.
- Health Apps: Offer tools for monitoring health metrics and managing conditions.
- Wearable Devices: Track physical activity, heart rate, and sleep patterns.
2. Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine tailors treatments based on individual genetic profiles.
- Genetic Testing: Identifies susceptibility to certain diseases.
- Targeted Therapies: Customized treatments based on genetic makeup.
3. Community Health Initiatives
Community health initiatives promote public health through education and resource provision.
- Public Health Campaigns: Raise awareness about health issues like smoking cessation and vaccination.
- Community Programs: Provide resources such as fitness classes and nutrition workshops.
In Conclusion
Maintaining human health requires a multifaceted approach encompassing balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, mental health care, preventive healthcare, and lifestyle modifications. Advances in digital health, personalized medicine, and community initiatives offer promising avenues for improving health outcomes. By understanding and addressing common health problems through effective mitigation strategies, individuals can enhance their quality of life and longevity, paving the way for healthier future generations.
References
World Health Organization (WHO). (2023). Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs). Retrieved from WHO website
American Cancer Society. (2023). What is Cancer? Retrieved from American Cancer Society website
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2023). Diabetes. Retrieved from CDC website
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI). (2023). Chronic Respiratory Diseases. Retrieved from NHLBI website
Mayo Clinic. (2023). Mental Health. Retrieved from Mayo Clinic website
National Institute on Aging (NIA). (2023). Healthy Aging. Retrieved from NIA website
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2023). Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. Retrieved from HHS website
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. (2023). Nutrition. Retrieved from Harvard website
National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2023). Sleep. Retrieved from NIH website
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). (2023). Environmental Health. Retrieved from EPA website
This comprehensive article provides an overview of human health, common health problems, and effective mitigation strategies, aiming to offer a holistic perspective on maintaining and improving health throughout different stages of life.